food protein induced enterocolitis syndrome treatment
Paxlovid is PBS listed for treatment of COVID-19. Diarrhea may occur within 24.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non IgE-mediated gastrointestinal food allergy that presents with delayed vomiting after ingestion primarily in infants.
. Like other food allergies FPIES reactions are triggered by eating a particular food. The child may appear tired and ill with pale skin. If a severe reaction does occur treatment includes the administration of intravenous fluids to counteract fluid loss from vomiting and diarrhea.
Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES is a systemic non IgE-mediated response to a specific trigger within food - most likely food proteinFPIES presents in two different forms. In some cases a feeding tube. Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome can be included under Asatmyaja-rogas one which is not conducive to the prakrithi constitution and agni digestive fire of a particular person.
Related
Vomiting typically occurring two hours after ingestion. FPIES food protein induced enterocolitis syndrome is a serious allergic reaction to certain foods. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is an uncommon disorder characterized by an allergic reaction to food that affects the gastrointestinal system.
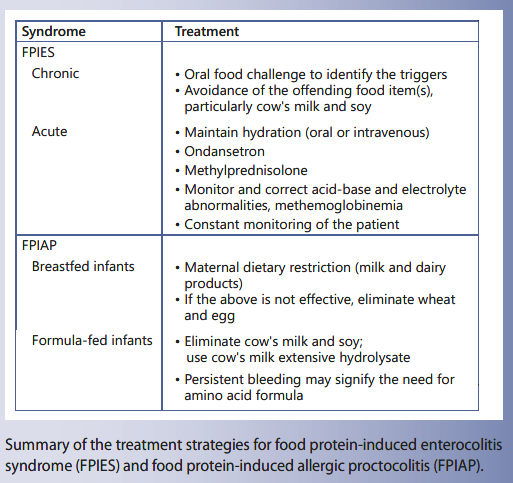
Classic symptoms of FPIES include profound vomiting diarrhea and dehydration. 20 mlkg boluses of isotonic saline. ASCIA is the peak professional body.
Treatment of FPIES is. The term enterocolitis specially refers to inflammation of the small and large intestines. The preventive diet will only be implemented if.
The most common triggers include cow milk soy and grains rice barley oats. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a severe non IgE delayed form of food allergy. While the pathophysiology of FPIES is poorly understood the clinical presentation of acute FPEIS reactions has been well characterized.
Hiatal hernia pyloric stenosis Hirschsprungs disease. Your doctor will advise as to how to alter the diet to achieve this. The recent publication of the First International Consensus Guidelines allowed a positive interaction between different research groups with.
We review here the peculiar characteristics of this syndrome. The only treatment for FPIES is to avoid the trigger food. Individuals with FPIES experience profuse vomiting and diarrhea that usually.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-immunoglobulin E IgE mediated gastrointestinal food hypersensitivity that manifests as profuse repetitive vomiting sometimes with diarrhea leading to dehydration and lethargy in the acute setting or chronic watery diarrhea with intermittent vomiting leading to. Diarrhea that begins after vomiting. This article focuses on the clinical manifestations of food allergy.
Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES is a type of food allergy affecting the gastrointestinal GI tract. FPIES usually starts in infancy although onset at older ages is. Removal of causative food from diet.
Treatment involves identifying and avoiding the food that causes the reaction. Avoidance of triggering foods ensuring good nutrition healing the gut balancing the immune system and maintaining a good inflammatory balance are keys to treatment. Intravenous fluids if dehydrated.
The same is true for the breast-feeding mother if there is a clear connection between breast milk intake and the babys symptoms. It is much less common than IgE-mediated food allergy and typically occurs in babies and infants. Food proteininduced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a nonIgEmediated gastrointestinal food allergy expressed with the acute or chronic phenotype1 The acute form is the commonest type and is characterized by repetitive vomiting lethargy with pallor ashen appearance and diarrhea within 26 hours from the induction of food.
An acute form and a chronic form. Unlike typical food allergies symptoms may not be. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a delayed non-IgE mediated gut allergic reaction to a foods usually presenting in the first two years of life with an estimated incidence in this age group of 1 in 7000 children.
Intravenous fluids if moderate to severe. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE-mediated food allergy that manifests with projectile repetitive emesis that can be followed by diarrhea and may be accompanied by lethargy hypotonia hypothermia hypotension and metabolic derangements. About Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome American Academy of Allergy Asthma and Immunology.
The primary symptom is profuse repetitive vomiting. Oral rehydration fluids if mild. These symptoms can lead to severe lethargy change in body temperature and blood pressure.
Or the stomach flu. FPIES usually develops in infancy and resolves around 3-5 years of age. Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES is a type of non-IgE mediated food allergy that can present with severe vomiting diarrhea and dehydration.
The treatment of FPIES includes infants being taken off offending foods and being exclusively breast fed or given an elemental medical formula. Acute FPIES reactions generally occur in children ages 412 months 14 hours after ingestion of the trigger food. Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES is an inflammation involving both the small intestine and the large intestine colon.
Symptoms include severe vomiting and diarrhea and usually occur 2-3 hours after eating a food. Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES sometimes referred to as a delayed food allergy is a severe condition causing vomiting and diarrhea. In its acute form FPIES presents with vomiting that usually begins 1 to 4 hours after trigger food ingestion can be 30 minutes to 6 or more hours.
Symptoms of food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome can vary from child to child and in severity. Prevention and Management The only way to prevent a Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES reaction is to strictly avoid the culprit food in the diet. Treatment of food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome.
In the last years the interest of the scientific community toward food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES has grown exponentially. Steroids may also be given to calm the. Guptas IAFA provides safe and effective remedies for Ayurvedic treatment of food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES.
Changes in blood pressure and body temperature. Food protein-induced enterocolitis FPIES is a delayed-type food allergic reaction in the gastrointestinal system which typically presents in the first year of life. Methylprednisolone 1 mgkg max 6080 mg.
Management Of Acute Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Emergencies At Home And In A Medical Facility Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology
Description Of Differences And Similarities Between Fpies Fpe And Download Scientific Diagram
Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology
Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Fpies Treatment Allergy Cure
Clinical Types Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Fpies Download Scientific Diagram
Dietary Management Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome During The Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology
Two Case Reports Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis
Managing Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome During The Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology
Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome And Proctocolitis
Comparison Between Acute And Chronic Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Download Scientific Diagram
Algorithm For The Management Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Download Scientific Diagram
Nutrients Free Full Text Non Ige Mediated Gastrointestinal Food Allergies In Children An Update Html
Tweets With Replies By Eastmidsfoamed Em3foamed Twitter
Oral Food Challenge In Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Download Table
Clinical Types Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Fpies Download Scientific Diagram
Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Oral Food Challenge Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology
References In Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Not So Rare After All Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology
Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome The Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology In Practice
